Table Of Content
There are additional options to restore your hair after COVID-19, too, including oral medications. Some people also benefit from a process by which platelets are taken from their plasma and injected into their scalp to boost hair regeneration. These options should be explored with the support of a healthcare provider.
Men's Health
Some shedding is temporary and may respond well to dietary changes, certain treatments, or lifestyle strategies. Other hair loss may be more permanent or may not stop until an underlying condition is treated. A 2020 review noted that various essential oils, including chamomile, thyme, and tea tree oils, could improve conditions such as alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and psoriatic alopecia.
Harvard Health Publishing
You should also see a doctor if your hair loss is accompanied by a rash, flaking or itching, which could indicate a different problem. The new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, is mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets. These can be produced when someone who has an infection coughs, sneezes, or talks. Researchers observed that a high amount of participants (67 percent) had androgenic alopecia. Certainly, experiencing an illness like COVID-19 can cause both physical and emotional stress.
Staying Healthy
Losing your hair can be a distressing experience, but you’re not alone. These molecules react with others to cause oxidative stress, which can harm cellular DNA. A 2018 review found that cells in the hair follicles of scalps with hair loss are extremely sensitive to oxidative stress. An older 2007 study found that caffeine blocked the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in male hair follicles.
Hair tends to return to normal on its own
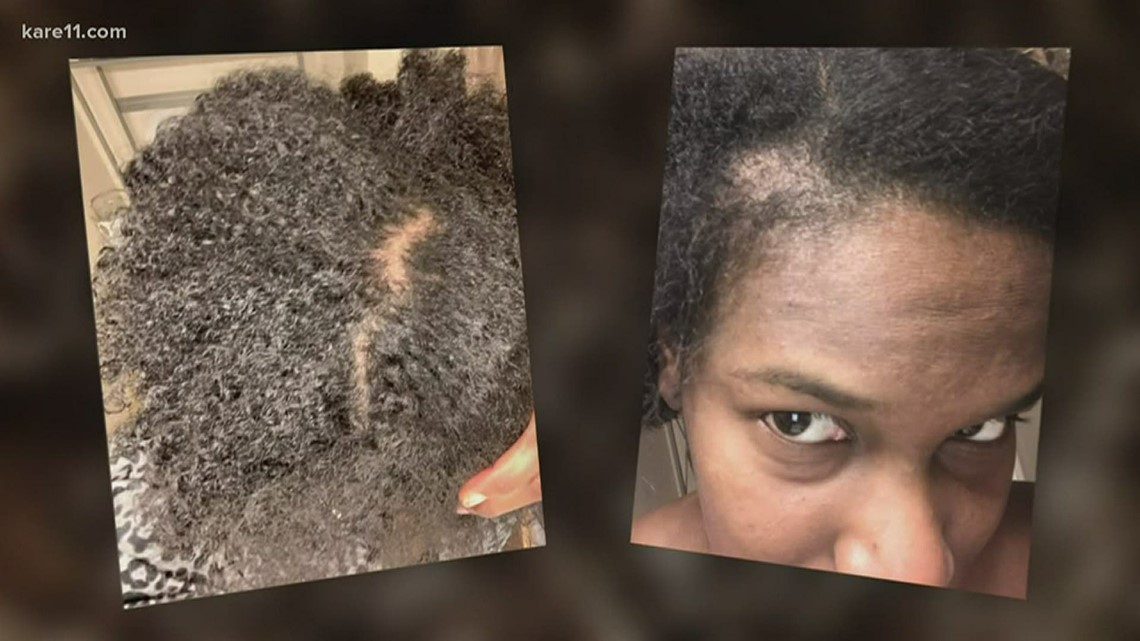
Hairs don’t grow during the telogen phase, but they don’t usually fall out either. The resting hairs remain in the follicle until they are pushed out by the growth of a new hair. The hairs will typically be pushed out or shed approximately 2-3 months after the stressful event. Seeing large amounts of hair being shed at once can cause significant distress. A person with this condition does not lose all their hair, although it unfortunately may become noticeably thin.
Vitamin A is partly made up of retinoids, which support healthy hair growth and influence the hair cycle. But it’s dose-dependent, meaning that consuming too much — or too little — can damage your hair. If you also notice a rash, or a burning or itchy scalp, make an appointment with a dermatologist. The medical term for this kind of temporary hair shedding is telogen effluvium, and Covid-19 is not the only cause.
Nearly two thirds of Korean SARS-CoV-2 cohort had long COVID at 2 years - University of Minnesota Twin Cities
Nearly two thirds of Korean SARS-CoV-2 cohort had long COVID at 2 years.
Posted: Tue, 09 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The state of your scalp changes after illness.
The effluvium caused post the infection with SARS COV2 could be explained by the physiologic response of the follicles to the stress of the infection. After a fever-causing infection, the effluvium usually starts 3 to 4 months after the inciting infection. The cytokines released due to the infection/fever, prematurely push the follicles into catagen and then into telogen. As the duration of telogen is ∼3 to 4 months, the shedding usually starts at this time. The authors have tried to put forward potential mechanisms by which the SARS-CoV-2 virus may interact with the hair follicle directly or cause injury to it.
What to Do if You’re Experiencing Hair Loss After Covid

Exercise, eating a well-balanced diet that includes a lot of protein and drinking enough water are ways to help combat hair shedding. Most cases of hair shedding after COVID-19 resolve themselves within about two to six months, researchers report. Transplants may be successful for some people depending on the cause of the hair loss.
Terms of Service apply.
Visiting your state or local health department’s website can help you find a testing location. If you have any questions or concerns about finding a testing location, talk with your healthcare provider. A July 2020 study compared balding patterns in 336 men hospitalized for COVID-19 and 1,605 men hospitalized without COVID-19.
Hair Loss After Covid: What to Know - The New York Times
Hair Loss After Covid: What to Know.
Posted: Fri, 30 Sep 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Minoxidil is a topical solution or foam that can help regrow hair by being applied directly to your scalp. It works by pushing hair into the growing phase instead of resting or shedding. While there are several different forms in which you can acquire minoxidil, Rogaine® is probably the most well-known brand. If the hair loss is severe or your hair isn’t coming back in like it should, there are other avenues you can explore with a healthcare provider. Some research has shown a loose connection between the COVID-19 vaccine and alopecia areata in a very small population of people who received COVID-19 vaccinations. The researchers are quick to point out, though, that the individuals studied may have already been at higher risk for alopecia.
When the cause of your hair shedding is due to a fever, illness, or stress, hair tends to return to normal on its own. As your hair grows back, you’ll notice short hairs that are all the same length by your hairline. Most people see their hair regain its normal fullness within six to nine months. Except for a large retrospective cohort study from Korea which investigated the risk of alopecia areata (AA) among COVID‐19 patients, other studies focused on telogen effluvium (TE).
Get instant access to members-only products and hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP The Magazine. Ochsner is a 501(c)3 not-for-profit organization, founded on providing the best patient care, research and education. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. It’s always a good idea to talk with your doctor before trying any supplements.

No comments:
Post a Comment